Docker is one of the awesome technologies which is essential for developers and sysadmins these days. Containers have a wide range of applications and they play an important role in numerous areas.
I am not going in the advantages of Docker in this article. This tutorial will cover the steps to install Docker in Fedora.
Installing Docker on Fedora Linux
Docker can be installed on Fedora in 3 ways:
- Installing via DNF (convenient, easy and recommended)
- Installing via RPM
- Using a script
Method 1: Installing Docker via DNF (recommended)
This is by far the most convenient way to install Docker, since updated versions can be easily installed without complicated steps.
To achieve this, you have to add the official docker repositories, and then install Docker via DNF command.
Run the following command first:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-core -yAnd then add the Docker repo to your Fedora system:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repoNow run the following command to install Docker and the required packages in your system:
sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io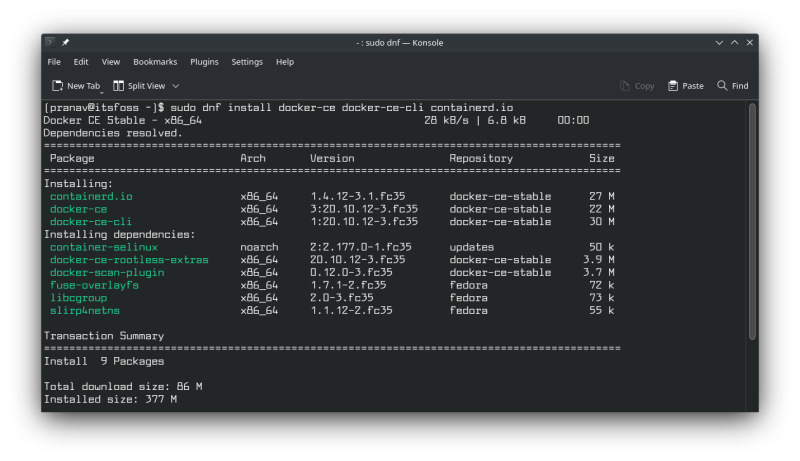
Also authorize when asked to import the GPG key in order to install Docker:
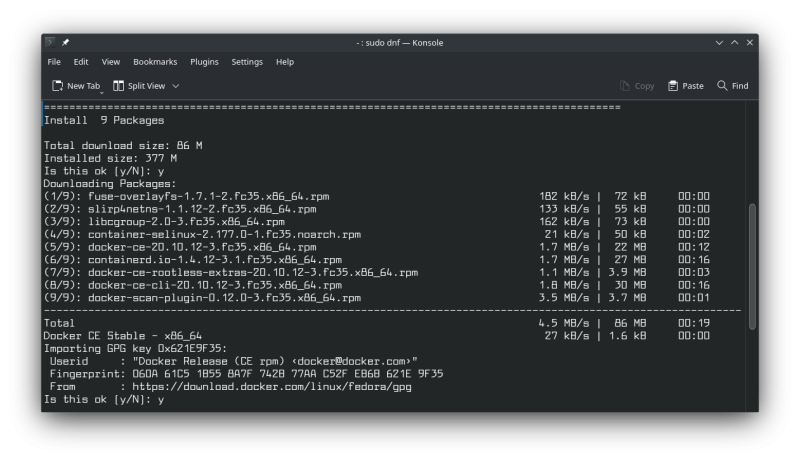
That’s it. You have got Docker on your system. You may check if it’s running fine by using this command:
sudo docker run hello-worldMethod 2: Installing Docker by downloading the RPM package
This method is useful when you want to test a specific version of Docker, or install Docker for older versions of Fedora.
However, this is inconvenient since you have to download the RPM manually every time when a new version pops up.
You can download the RPM officially, by navigating to the site, your version, architecture, release type, and download it (you will need docker-ce, docker-ce-cli & containerd.io RPMs for sure; you may download additional stuff if needed).
To install the RPMs, fire up the terminal, navigate to the folder where you downloaded them, and type
sudo dnf install /path/to/file.rpm -y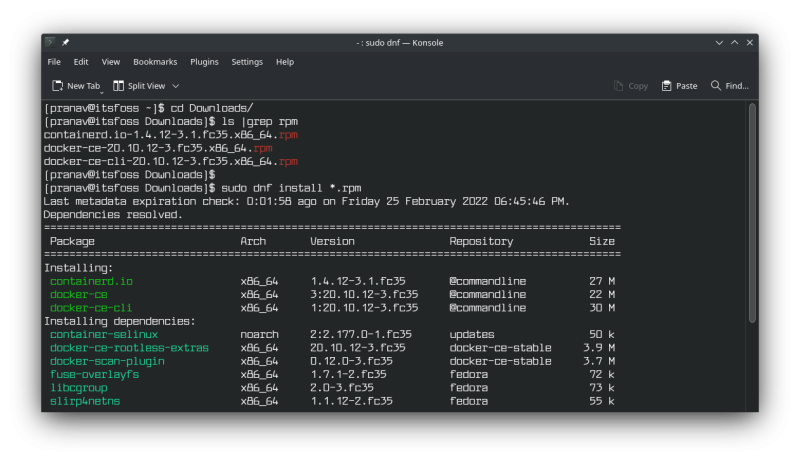
Method 3: Install Docker using the official installation Script
Docker offers a script to download docker and do the necessary steps to install it. But this script is not meant to be used to upgrade the existing versions of Docker installed via DNF/RPMs (however it’s possible if you previously used the script to get Docker).
Download the script, make it executable and execute it with sudo privileges:
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
chmod u+x ./get-docker.sh
sudo sh ./get-docker.shThat will do the necessary to install Docker.
Testing Docker
Docker can be tested by running a hello-world image offered by Docker themselves. If it works fine, then it’s a sign that Docker works well.
Firstly, start the Docker service since it’s not enabled by default:
sudo systemctl start dockerDownload the hello-world image from docker and run it:
sudo docker run hello-world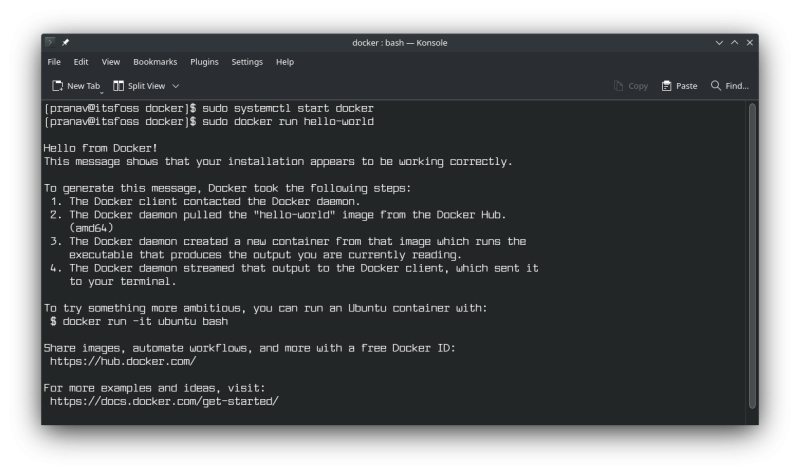
hello-world running successfullyNote: If you are under a proxy or multiple network interfaces, then the image download will just fail after some time, returning a 408 response error (it’s exactly what happened to me). Even if you’re not under a system-level proxy and your download fails, the problem might be the ISP who might’ve enabled it. In my case, I switched networks to download the image.
Removing Docker from Fedora
Regardless of which method you followed to install Docker, you can remove it by the command
sudo dnf remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.ioThat removes Docker and all related packages. But if you want to completely remove the containers too, then you have to remove the /var/lib/docker and /var/lib/containerd folders:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerdAnd that’s all about the tutorial. Feel free to leave a comment with your suggestion or a simple thank you :)

