
Running two or more commands in one line can save you a good deal of time and help you become more efficient and productive in Linux.
There are three ways you can run multiple commands in one line in Linux:
| Operator | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| ; | Command 1 ; Command 2 | Run command 1 first and then command 2 |
| && | Command 1 && Command 2 | Run command 2 only if command 1 ends sucessfully |
| || | Command 1 || Command 2 | Run command 2 only if command 1 fails |
Let me show you in detail how you can chain commands in Linux.
Using ; to run multiple Linux commands in one line
The simplest of them all is the semicolon (;). You just combine several commands that you want to run using ; in the following fashion:
cmd1; cmd2; cmd3Here, cmd1 will run first. Irrespective of whether cmd1 runs successfully or with error, cmd2 will run after it. And when cmd2 command finishes, cmd3 will run.
Let’s take an example you can practice easily (if you want to).
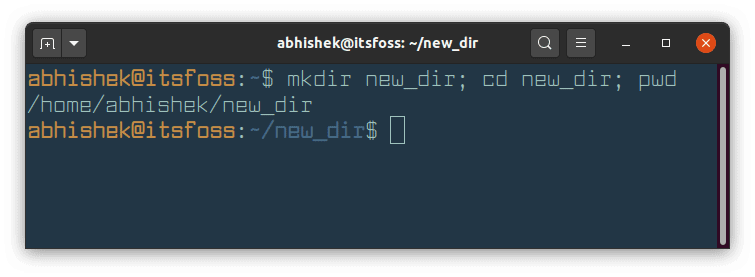
mkdir new_dir; cd new_dir; pwdIn the above command, you create a new directory named new_dir with mkdir command. Then you switch to this newly created directory using cd command. Lastly, you print your current location with pwd command.
Using && to run multiple Linux commands
Sometimes you want to ensure that the in the chain of Linux commands, the next command only runs when the previous command ends successfully. This is where the logical AND operator && comes into the picture:
cmd1 && cmd2 && cmd3If you use Ubuntu or Debian based distributions, you must have come across this command that utilizes && concept:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeHere, the first command (sudo apt update) refreshes the package database cache. If there is no error, it will then upgrade all the packages that have newer versions available.
Let’s take the earlier example. If the new_dir already exists, mkdir command will return an error. The difference in the behavior of ; and && can be seen in the screenshot below:
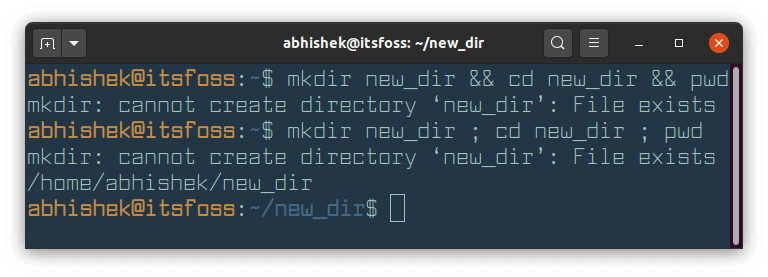
Did you see how commands separated by && stopped when the first command resulted in an error?
Using || to run several Linux commands at once
You can use the logical OR operator (||) to run a chain of commands but the next command only runs when the previous command ends in error. This is opposite to what you saw with &&.
cmd1 || cmd2 || cmd3If cmd1 fails, cmd2 runs. If cmd2 runs successfully, cmd3 won’t run.
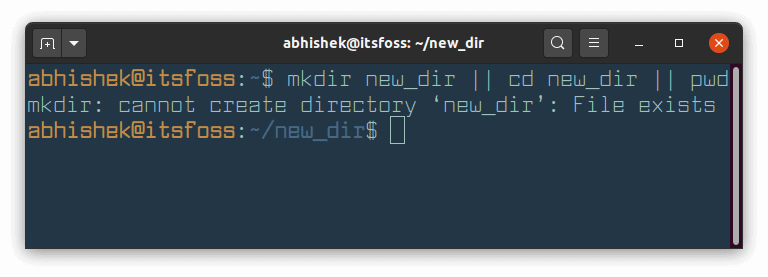
In the screenshot above, mkdir new_dir command fails because `new_dir already exists. Since this command fails, the next command cd new_dir is executed successfully. And now that this command has run successfully, the next command pwd won’t run.
Bonus Tip: Combine && and || operators
You may combine the operators to run two or more Linux commands.
If you combine three commands with && and ||, it will behave as the ternary operator in C/C++ ( condition ? expression_true ; expression_false).
cmd1 && cmd2 || cmd3For example, you can check if file exists in bash, and print messages accordingly.
[ -f file.txt ] && echo "File exists" || echo "File doesn't exist"Run the above command before and after creating the file.txt file to see the difference:
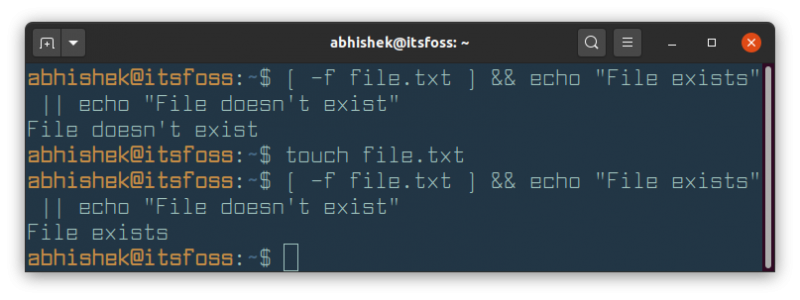
You can also use ;, && and || to run multiple commands in bash scripts as well.
More such Linux terminal tips
Like copy-paste in Linux terminal, running multiple commands at once is also one of the many Linux command line tips for saving time.

Though elementary, it is an essential concept any Linux terminal user should know. Here are a few more.

And if you are absolutely new to Linux commands, I have created a series of tutorials that will help you.

I hope you liked this terminal trick. Stay tuned for more Linux command tips and tools.


